Evaluating Transmagnetic Stimulation Techniques for Optimal Health Solutions
Transmagnetic Stimulation (TMS) has emerged as a groundbreaking approach in the realm of neurotherapy and mental health treatment. According to a report by the National Institute of Mental Health, roughly 1 in 5 adults in the U.S. experience mental illness, highlighting the urgent need for innovative therapeutic techniques. TMS offers a non-invasive solution, harnessing magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. Recent advancements in TMS technology have significantly improved its efficacy, positioning it as a promising alternative for conditions like depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Research indicates that approximately 50% of patients experience a substantial response after TMS treatment, underscoring its potential in transforming mental health care.
Moreover, the global market for TMS is projected to reach USD 1.9 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of approximately 12.1% from 2021, according to a report by Fortune Business Insights. This surge reflects a growing recognition of TMS among healthcare providers and patients alike, driven by its demonstratable success rates and minimal side effects compared to traditional pharmacological approaches. As we delve deeper into evaluating the various TMS techniques available, understanding their specific applications, benefits, and limitations becomes paramount for optimizing health solutions and fostering holistic patient care.
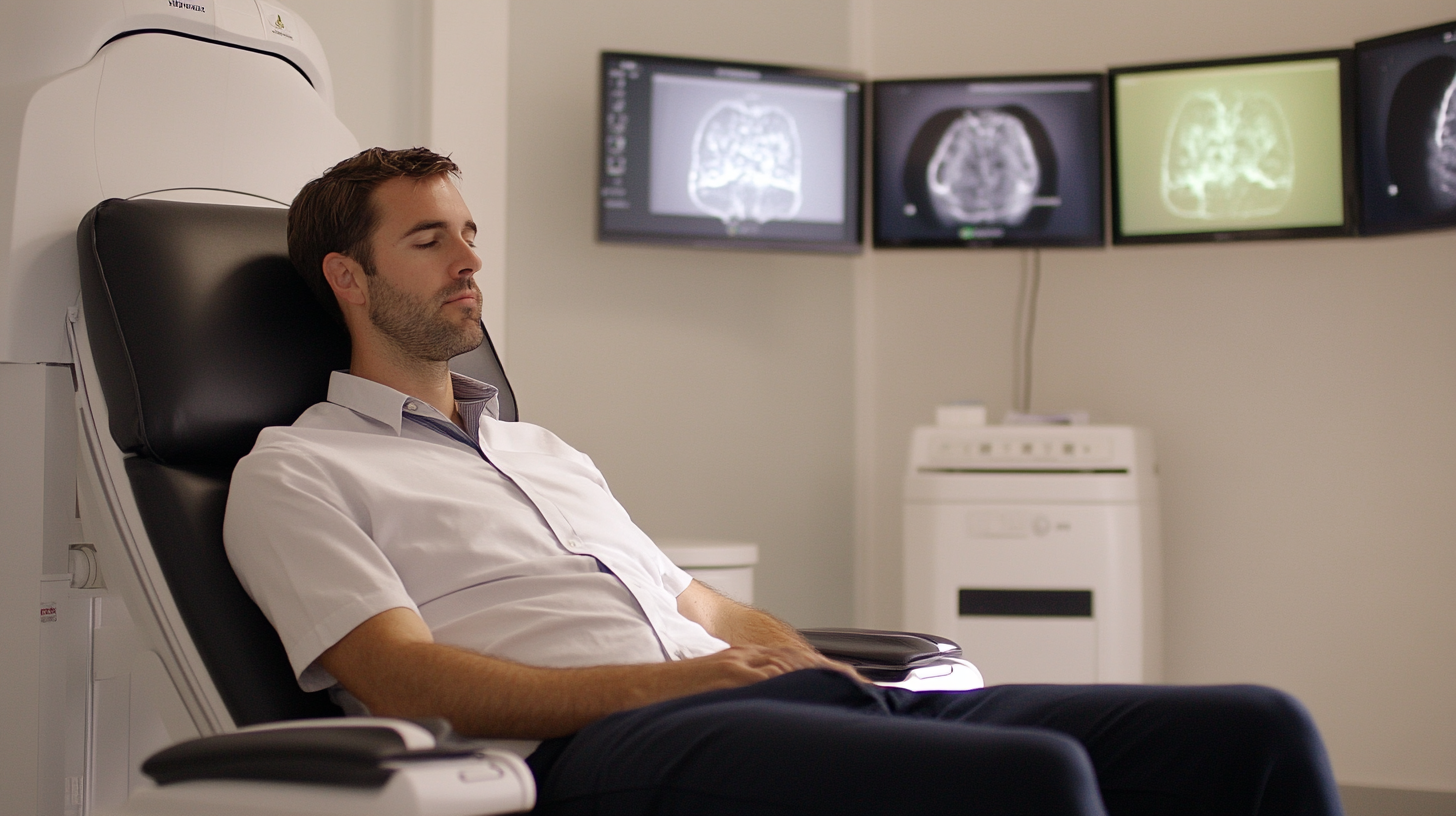
Understanding Transmagnetic Stimulation: A Comprehensive Overview
Transmagnetic stimulation (TMS) is an emerging therapeutic technique that harnesses the power of magnetic fields to influence neural activity in the brain. This non-invasive procedure involves the application of brief magnetic pulses to stimulate specific areas, offering a promising avenue for treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions. An understanding of TMS begins with recognizing its dual role in both research and clinical settings, where it serves as both a diagnostic tool and a treatment modality. The mechanisms behind TMS are rooted in electromagnetic principles, where the pulsating magnetic fields induce electric currents in the brain's neurons. This interaction can enhance or inhibit neuronal firing, effectively reshaping neural circuits associated with mood regulation, pain perception, and cognitive processes. Recent advancements in TMS technology, such as repetitive TMS (rTMS) and theta-burst stimulation, have significantly increased its efficacy and adaptability, allowing it to target a broader range of conditions, including depression, anxiety, and even chronic pain syndromes. As researchers continue to explore its applications, the potential for TMS to create personalized treatment plans grows. By tailoring stimulation parameters to individual patients' needs, healthcare providers can maximize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing side effects. Understanding these techniques is crucial for harnessing their full potential, paving the way for new health solutions that can transform the treatment landscape for mental and neurological disorders.
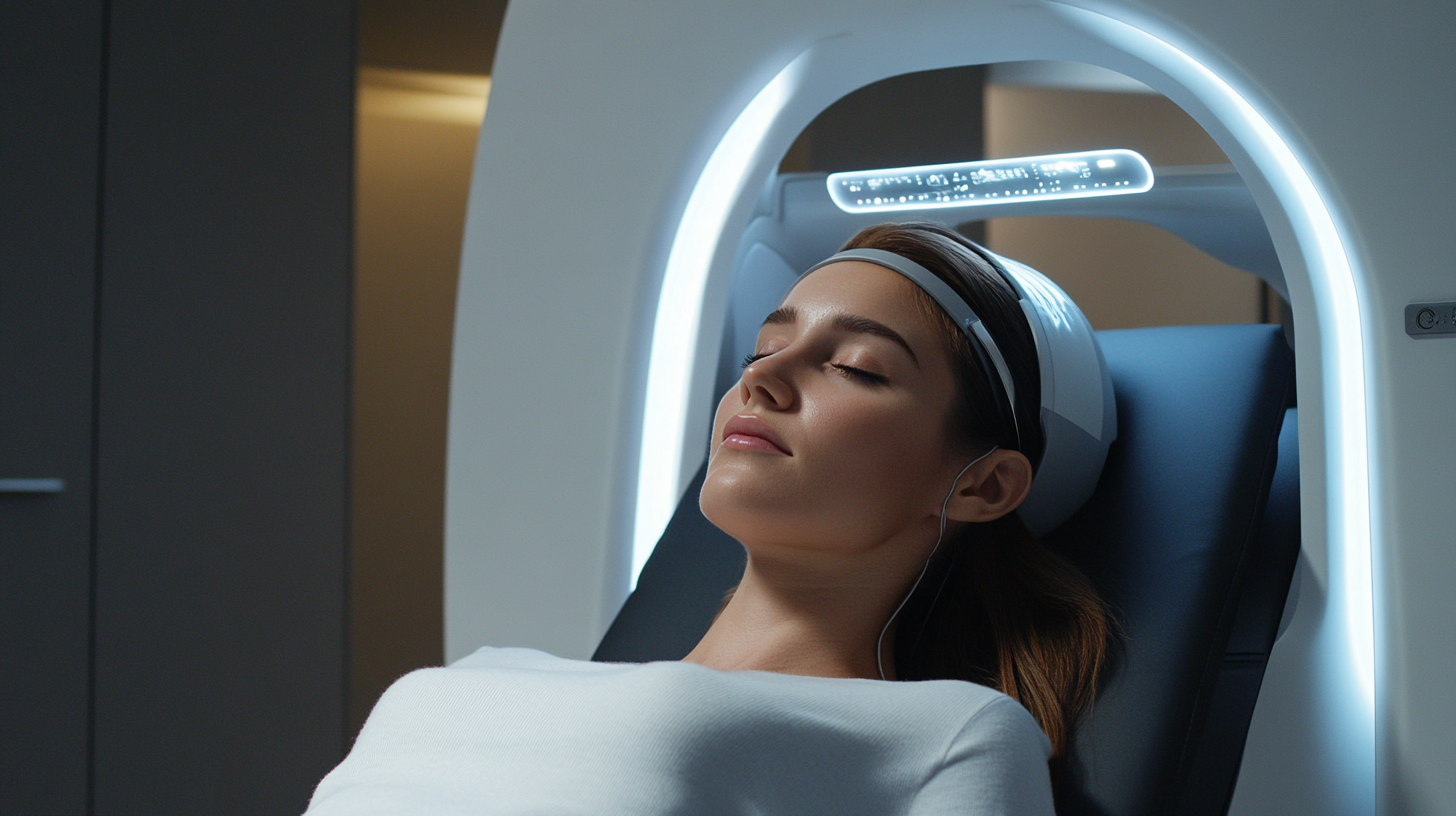
Different Techniques of Transmagnetic Stimulation and Their Applications
Transmagnetic stimulation (TMS) is an innovative approach to health and wellness that harnesses magnetic fields to influence brain activity. Different techniques of TMS have emerged, each tailored for specific applications and outcomes. Among the most prominent is repetitive TMS (rTMS), which involves delivering a series of magnetic pulses to targeted brain regions. This technique has shown promising results in treating depression, improving cognitive function, and even enhancing motor recovery in stroke patients.
Another notable method is deep TMS (dTMS), which allows for deeper penetration of magnetic fields into the brain. dTMS is particularly effective in addressing more severe neuropsychiatric conditions by influencing deeper brain structures. It has been utilized in clinical settings for its potential in alleviating symptoms of treatment-resistant depression, making it a valuable tool in mental health management.
Furthermore, localized TMS techniques have gained attention for their precision and effectiveness. These methods target specific brain areas, potentially leading to better patient outcomes with minimal side effects. Applications range from pain management to improving neurological recovery post-injury. As research advances, the versatility of TMS continues to expand, making it a critical area of study in optimizing health solutions through innovative and non-invasive techniques.

Evaluating the Efficacy of Transmagnetic Stimulation for Mental Health
Transmagnetic Stimulation (TMS) has emerged as a promising non-invasive therapy for mental health disorders, particularly in the treatment of depression. Recent studies indicate that TMS can significantly alleviate symptoms in patients who have not responded adequately to traditional treatments. According to a report by the American Psychiatric Association, approximately 60-70% of patients experience a positive response to TMS, showcasing its efficacy in addressing severe depression.
The mechanism behind TMS involves the use of magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, leading to enhanced neuronal activity. A meta-analysis published in the Journal of Affective Disorders highlighted that TMS treatments result in a notable reduction in depressive symptoms, often measurable within the first few weeks of therapy. Moreover, follow-up data suggests that the benefits can last for months post-treatment, with some patients maintaining improvements even a year later.
Additionally, TMS holds potential for treating other mental health conditions, such as anxiety and PTSD. A study from the National Institutes of Health found that patients with PTSD saw a 30% improvement in symptoms after a series of TMS sessions. These findings underscore the versatility of TMS and its role as a vital tool in modern mental health care, positioning it as an optimal solution for achieving mental well-being in those suffering from various disorders.
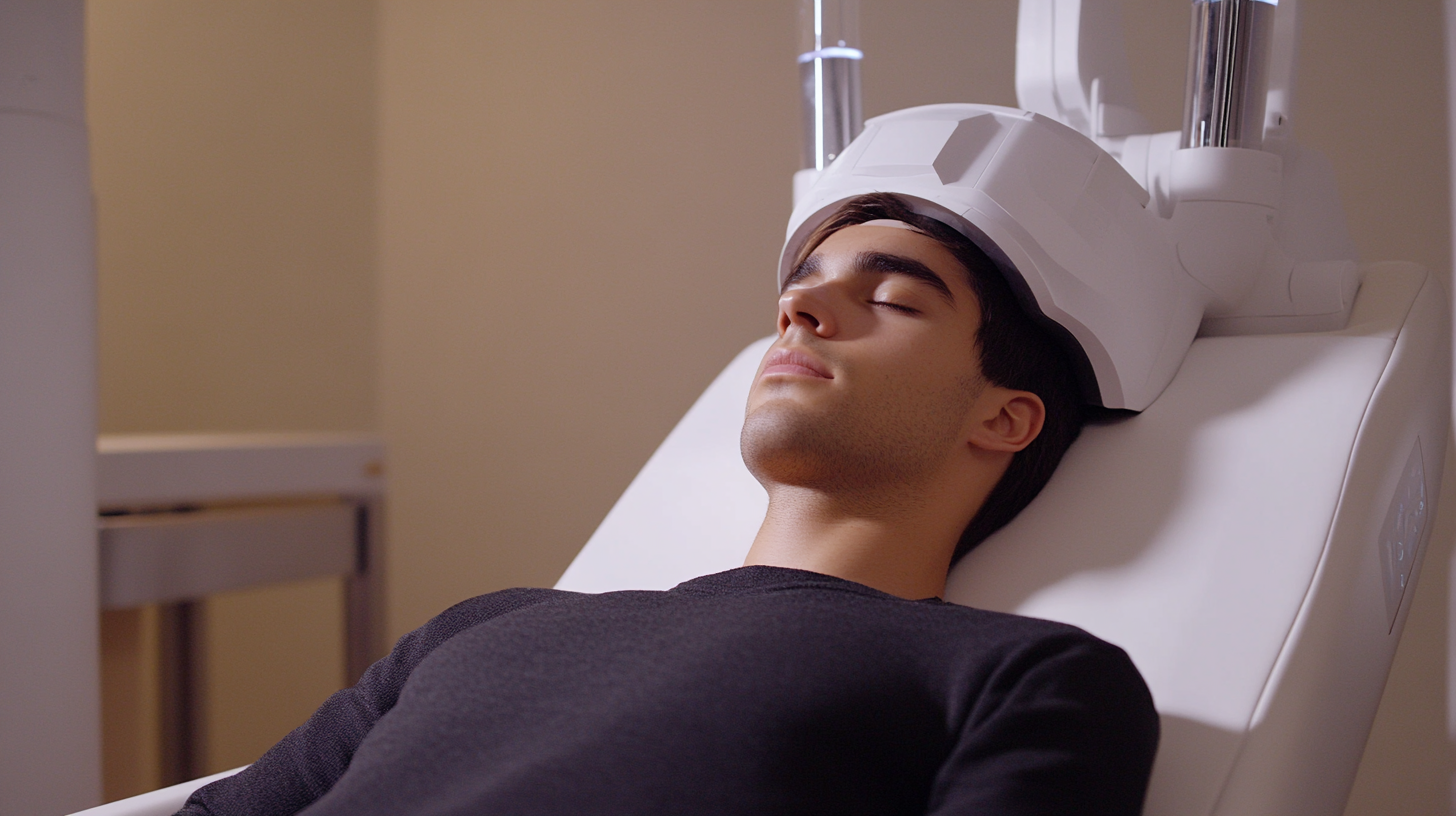
Safety Considerations and Side Effects of Transmagnetic Stimulation
Transmagnetic stimulation (TMS) has garnered considerable attention as a non-invasive treatment for various health conditions, particularly in the realm of mental health. While the effectiveness of TMS can be promising, it is crucial to address the safety considerations and potential side effects associated with this technology. Understanding these factors is essential for both providers and patients seeking optimal health solutions.
One significant safety concern related to TMS is the risk of inducing seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of epilepsy or seizure disorders. Although the incidence is low, practitioners typically conduct thorough patient assessments to identify any contraindications before initiating treatment. Additional safety considerations include monitoring for changes in mental state or mood during the sessions, as TMS can sometimes exacerbate certain symptoms or lead to transient discomfort.
Moreover, some patients may experience common side effects such as headaches, scalp discomfort, or fatigue following TMS sessions. These effects are often mild to moderate and tend to resolve shortly after treatment. However, being aware of personal thresholds for discomfort and clearly communicating any adverse experiences with healthcare providers is crucial. This collaborative approach ensures that the treatment remains beneficial while minimizing risks, thus paving the way for informed decisions about employing transmagnetic stimulation as a health solution.
Future Prospects: Innovations in Transmagnetic Stimulation Technologies
The future of transmagnetic stimulation (TMS) technologies holds immense promise in redefining health solutions across various medical fields. As researchers delve deeper into the mechanisms and applications of TMS, innovative techniques are emerging that enhance its efficacy and accessibility. For instance, advancements in portable TMS devices are being developed to bring treatment to patients in their own environments, reducing the barriers associated with traditional clinical settings. This shift not only broadens the reach of TMS but also encourages adherence to treatment protocols, allowing for more consistent health outcomes.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with TMS technology is paving the way for personalized treatment plans. By analyzing patient data, including brain activity patterns and treatment responses, AI can help tailor individual stimulation protocols that maximize therapeutic effects. This level of customization can significantly improve patient experiences, as it emphasizes targeted care rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
Looking ahead, the ongoing exploration of combination therapies—using TMS alongside pharmaceuticals or other treatment modalities—offers a pathway to enhance recovery for a range of conditions, from depression to chronic pain. As innovations continue to unfold, the synergy between TMS technology and other therapeutic options may set new standards for optimal health solutions, ultimately transforming patient management in mental health and neurology.

